Operator survey: Analytics and assurance critical for 5G security
Heavy Reading's 2023 5G Network Analytics and Automation Operator Survey results indicate that operators must incorporate AI/ML-driven security anomaly detection within analytics and assurance solutions to ensure secure, automated end-to-end protection for their networks.

Security attacks are becoming more frequent, sophisticated and pervasive. Within the telecommunications industry, breaches are increasing yearly, and DDoS and customer data exposure are the most common. Disruption, heavy financial penalties and reputational damage create a colossal burden for operators. 5G will require new analytics and assurance measures to defend and prevent security issues and uphold stringent SLAs.
5G architectures introduce disaggregated functions, API-exposure-based services, continual software updates, new interfaces and protocols, and exponentially more devices, increasing vulnerabilities and evolving the threat landscape. This evolution presents unique security challenges associated with the need to have a single real-time holistic view of the network across the RAN, edge, transport and core network domains.
As a result, current node-based protection mechanisms, like firewalls, security gateways and policy enforcement, are being challenged. To meet the realities of this complex security model, new solutions must incorporate mechanisms to address the following 5G-driven security changes:
Disaggregation: Cloud transformation and architectural changes present different vectors to let threats in. Security detection and mitigation involve the correlation of multiple layers (i.e., cloud infrastructure, virtualization/containerization and 5G network domain) as manual inspection becomes too slow, difficult and time-consuming — even for experts.
Dynamic environments: Frequent software updates, advanced services and programmability (e.g., network APIs) add the risk of malicious code compromising the network and exposing sensitive data vulnerabilities. For example, software updates for network functions and infrastructure will require digital signing. However, additional security frameworks to securely automate, identify and monitor irregular operations will provide a real-time defense.
Exponential subscriber endpoints: 5G user equipment (UE) to support consumers, connected industry, Internet of Things (IoT) and sensors, and multi-generational devices extend the threat surface for potential malware breaches, botnet attacks, signaling storms, etc. Future security solutions must identify malicious or compromised UEs quickly. Artificial intelligence/machine learning (AI/ML) algorithms can support this, processing massive amounts of data and predicting optimal outcomes.
Multiple domains to secure: The distribution of network functions, hybrid cloud networks and virtual networks (e.g., network slices) creates additional boundaries to secure. The cloud offers varied models for hosting mobile networks (i.e., full, hybrid or even fallback scenarios). Visibility into the cloud and over multiple domains to identify boundary weaknesses or flag errors (e.g., misconfiguration of gateways or tunnel IP addresses) will be critical to safeguard security.
To build and deliver a new generation of security, operators must ensure they can observe and assure the entire network, taking advantage of new technologies for speed and efficiency. A question from Heavy Reading's 2023 5G Network Analytics and Automation Operator Survey asks operators what role analytics and assurance will play in 5G SA security detection and mitigation. (Click here to download the survey.)
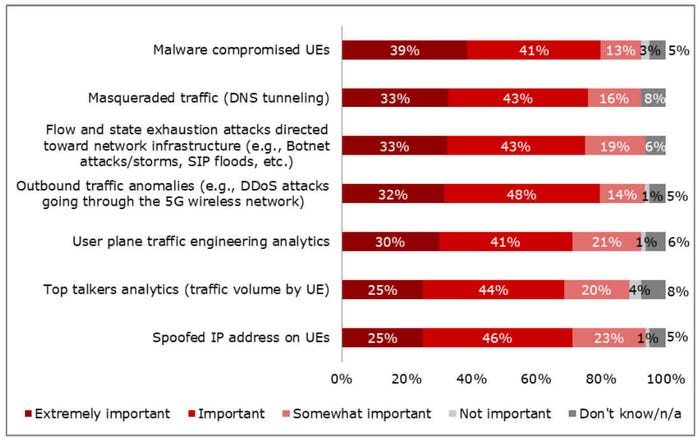
In the figure below, operators acknowledge the importance of analytics and assurance across all security detection and attack prevention options in their end-to-end networks. "Malware compromised UEs" and "outbound traffic anomalies (e.g., DDoS attacks going through the 5G wireless network)" are of the greatest importance to operators, with a combined 80% of respondents selecting "extremely important" and "important." This result acknowledges the potential damage of these attacks and the difficulty of detection with current methods.
Control and user plane separation introduced to the 5G architecture attempts to limit generational threats able to disable both planes simultaneously. However, operators still see a vital requirement for deep network security visibility, indicating the high importance of "flow and state exhaustion attacks" and analytics for identifying masqueraded (network address translated traffic) and user plane traffic with respondents.
"Top talker analytics" and "spoofed IP addresses on UEs" are the lowest relative scoring of security options but remain high, with almost 70% of the combined votes for "extremely important" or "important." The lower position of these responses compared to the other security options may be due to these established checks or the ability of certain network functions to gather some of this information. It is clear from these results that 5G security detection and prevention must be all-encompassing and include multiple options.
How important are the following areas of 5G SA security detection and attack prevention to your organization's analytics and assurance?
(Source: Heavy Reading)
In conclusion, operators know the importance of maintaining a secure network and addressing the ongoing security challenges and vulnerabilities. To meet these challenges, 5G SA security detection and prevention mandate that a security stance covers multiple aspects, is holistic and can identify and mitigate any spurious behavior in real-time. Architecturally, these requirements demand built-in security to safeguard against increasing and more advanced attacks. Therefore, operators must incorporate techniques such as AI/ML-driven security anomaly detection within analytics and assurance solutions to enforce secure, automated and end-to-end protection.
For more information, check out this archived webinar.
This blog is sponsored by NETSCOUT.
About the Author(s)
You May Also Like













